If you’re asking, ‘How Many Zinc Recycling Processes are there today?’—this article gives you the answer with a detailed comparison of the four main methods for recycling zinc!
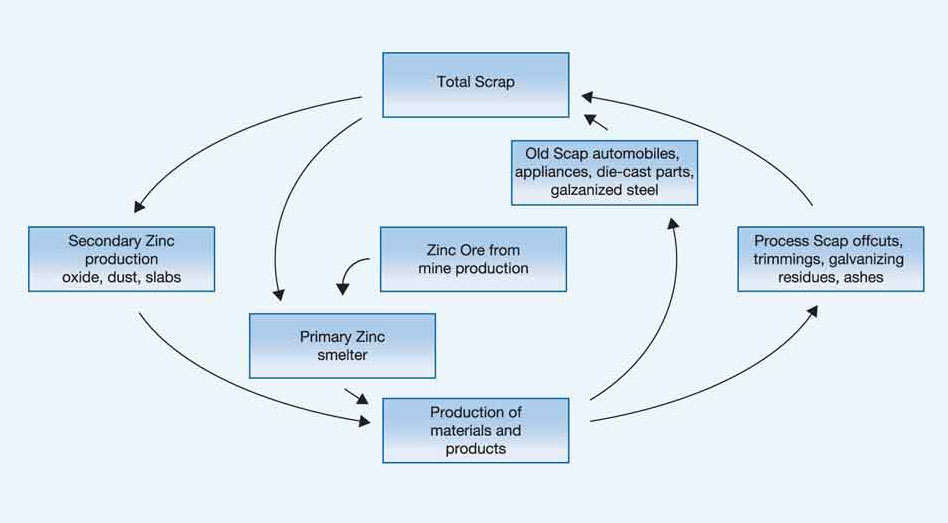
Zinc recycling plays a crucial role in reducing waste and conserving resources, especially in industries like steel production, where large amounts of zinc-bearing waste are generated. There are four primary processes used for recycling zinc: Waelz Kiln Process, Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF) Process, Zinc Scrap Refining, and the Hydrometallurgical Process. Each method has its advantages, depending on the type of material being processed and the desired final product.
Here’s a comparison table for the four main zinc recycling processes: Waelz Kiln Process, Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF) Process, Zinc Scrap Refining, and the Hydrometallurgical Process:
| Process | Main Application | How It Works | Primary Output | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waelz Kiln Process | Recycling EAF dust and zinc-bearing industrial waste | Zinc-bearing materials are heated in a rotary kiln at 1,200°C to 1,400°C, volatilizing zinc, which is then condensed into zinc oxide. | Zinc oxide | Efficient for high-volume waste with high zinc content | Requires high energy input, produces slag |
| Rotary Hearth Furnace (RHF) Process | Recycling EAF dust and zinc-containing waste | Materials are placed on a rotating hearth, heated to high temperatures, where zinc is volatilized and collected. | High-purity zinc oxide | Flexible material handling, efficient for certain applications | Limited to specific material processing needs |
| Zinc Scrap Refining | Refining metallic zinc scrap (galvanizing residues, zinc sheets) | Zinc scrap is melted in a furnace, where impurities are separated and zinc is refined. | High-purity metallic zinc | Simple process for metallic zinc, produces reusable zinc | Only applicable to metallic zinc scrap, not industrial waste |
| Hydrometallurgical Process | Recycling low-grade ores and zinc ash | Zinc is leached from materials using an acidic solution, purified, and recovered through electrowinning. | High-purity metallic zinc | Lower energy consumption, high-purity zinc recovery | Requires chemical handling, can produce hazardous residues |
Summary:
- Waelz Kiln and RHF are best for recycling zinc from industrial waste like EAF dust, with the Waelz kiln handling larger volumes.
- Zinc Scrap Refining is ideal for metallic zinc recycling, focusing on simple processes for pure zinc recovery.
- Hydrometallurgical Process is more suitable for low-grade ores and materials, offering a high-purity zinc product with lower energy consumption but requiring complex chemical management.
This table highlights the strengths and challenges of each process, showing their applications based on the type of material and desired output.
Conclusion
The four main zinc recycling processes – Waelz Kiln, RHF, Zinc Scrap Refining, and the Hydrometallurgical process – offer versatile solutions for recovering zinc from a wide range of materials. Each process is optimized for specific types of waste and end products, making zinc recycling a key component in industrial sustainability. By recycling zinc efficiently, industries reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize their environmental footprint.


